Lesson Planning Activities For Your Language Lessons. Lesson plans with some of the most basic elements of instruction that might be of use for the language language instructor
Lesson Planning Activities For Your Language Lessons
Lesson Planning Activities. Lesson Planning Activities for All Language Classrooms
Lesson Planning Activities For Your Language Lessons
Lesson Planning Activities For Your Language Lessons with some of the most basic elements of instruction that might be of use for the language language instructor
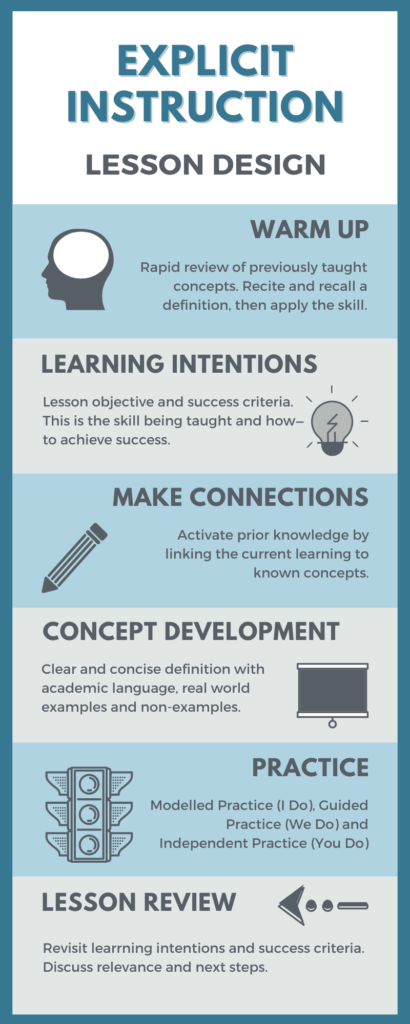
Instructional design varies from discipline to discipline, and there are many models that might evoke a similar look to lesson planning. Nonetheless, this lesson plan design includes some of the most basic elements of instruction that might be of use for the language language instructor. The terms used here are somewhat universal, but other terms exist and, once again, vary from context to context. For example, the term “warm up” is referred to by other instructional designers as a “theme introduction,” “attention getter,” or as a process of “activating/engaging learners.”
- 1) Warm Up
- 2) Objective Discussion
- 3) Present and Model
- 4) Guided or Controlled Practice
- 5) Less Guided Practice
- 6) Independent Practice
- All of which lead at the same time to
- 7) Assessment
A teacher is one who makes himself progressively unnecessary
~
Thomas Carruthers

Lesson Planning Activities For Your Language Lessons
What follows are a few very simple ideas to help stimulate interaction and thought in an classroom.
Step 1: Warm up or Prepare Students

Description
In this portion of a lesson, a teacher “warms up” the students by activating the students’ background knowledge and introducing new knowledge. A teacher may do this by presenting some key vocabulary, eliciting students’ knowledge of the subject, using prediction exercises, etc.
Here are some examples:
Word of the Day Worksheet

All downloads are in PDF format
Here are some Warm-up Worksheets

Step 2: Discuss the Objectives

Description
In this portion of a lesson, a teacher attempts to give learners a metacognitive understanding of the lesson itself. In simpler terms, the teacher is, either explicitly or implicitly, trying to help students learn WHY they are doing what they are doing, and HOW these objectives, if obtained, might help them.
Teachers who engage in these kinds of metacognitive strategies tend to have much more highly motivated students. Teachers themselves also attain better clarity and focus by having the objectives clearly stated and understood.
Here are some examples
All downloads are in PDF format

Step 3: Present Instruction/Model

Description
In this portion of the lesson, teachers give students new information they must know or new skills that they must acquire. Teachers here attempt to scaffold, explain, or otherwise break down information for students to grasp the new concepts. In addition to presenting or instructing, teachers are encouraged to provide models (examples) for students to follow. For example, a teacher might give a sample dialogue, a model essay, or put the necessary vocabulary to be acquired in sentences.
Here are some examples

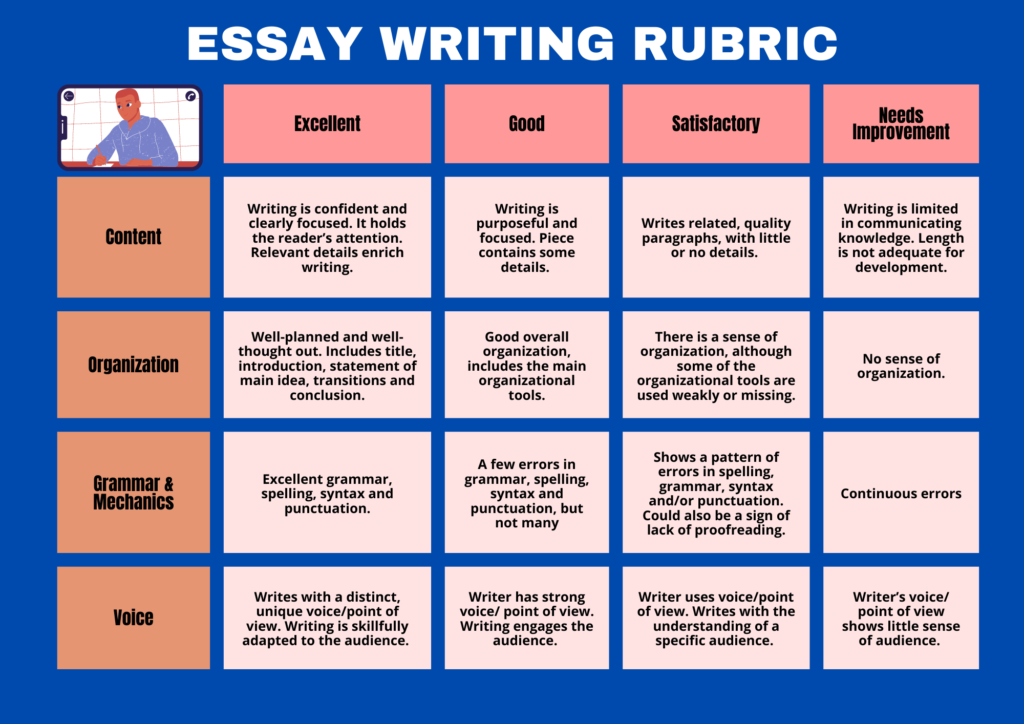
Here are some PDF free to download
All downloads are in PDF format

Step 4: Guided or Controlled Practice

Description
In this portion of a lesson, students are invited to practice their new skills and become familiar and comfortable with it. For difficult language concepts, this practice is often very controlled, meaning that it is done with a lot of guidance from either the teacher or other experts
Here are some PDF worksheets
All downloads are in PDF format

Step 5: Less-guided Practice

Description
Following a controlled practice, students are often given practice that has less
constraints and higher difficulty. For example, rather than doing an activity with a teacher, students might be required to do an activity in pairs or groups. In addition, the activity itself might be put modified to provide additional support.
A teacher still facilitates learning by answering questions and providing support to the groups or pairs, and the activity itself should help students to gain more comfort with the language required.
Here is an example
All downloads are in PDF format

Step 6: Independent Practice

Description
After a sufficient amount of pair or group work, the students are given an independent activity. This often means that the student will work alone to
demonstrate the knowledge or skill that they have acquired. This can be done through a quiz or testing scenario, or some sort of performance such as a presentation or written representation of their newly acquired language skills.


Step 7: Assessment
Description
Evaluating student work can happen at any stage of a lesson. Formative assessment generally refers to the kind of assessment that is done during instruction, and could include asking questions, giving informal quizzes, and eliciting student participation. Summative assessment often follows an independent practice, and is meant to measure a student’s ability to attain the objectives set out in the lesson plan. It is meant not only as a measure of the students, but can also provide feedback to a teacher as to how well the instruction was received, and what parts of the instruction need continued support.
Here are some Assessment Tests you can find on Language Advisor

Lesson Planning Activities For Your Language Lessons
Here are some other Lesson Planning Activities you can find on Language Advisor
Lesson Planning Activities For Your Language Lessons