Listen Up! Using Audio Books for English Teaching for Advanced Learners. Benefits of Using Audio Books with English Language Learners
Listen Up! Using Audio Books for English Teaching for advanced Learners

Listen Up! Using Audio Books for English Teaching for advanced Learners
Why Use Audio Books?
- Exposure to patterns, intonation, expressions, different accents & dialects, and pronunciation of a language
- Provides example of fluent reading
- Dramatized audio books can increase students interest in the text
- Allows “readers” to enjoy a book at their interest level, even if it is above their reading level
- Students can work at the same pace
- With text & audio: a multisensory approach to reading
- Supports auditory learners
- Helps with literacy development
- Improves comprehension of text
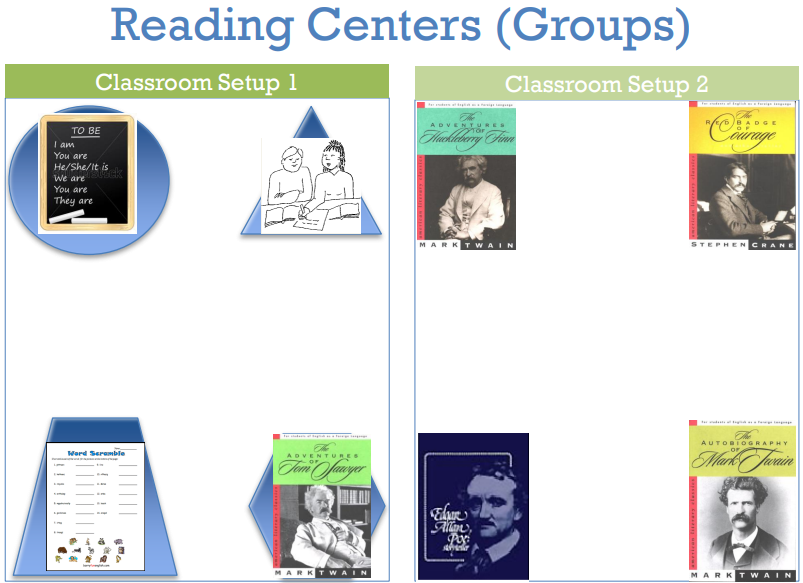
Ways to Use Audio Books inthe Classroom and Beyond
- Whole Class
- Reading Centers (In Groups)
- Classroom Management
- Independently

Listen Up! Using Audio Books for English Teaching for advanced Learners
Classroom Management
- Rewards
- Warm-ups, closings, transitions
- During “boring” tasks
- Ex: clean-up
Independently
- Commuting/Traveling to
- and from school
- While doing daily chores
- An incentive program

Reading & Listening Skills
- Vocaulary Building
- Listening/Reading Comprehension
- Listening/Reading for Details
- Summarizing & Sequencing
- Prediction
- Analysis
Vocabulary Building
- Listening for Vocabulary
- High frequency words (articles, forms of “to be”, question words, etc.)
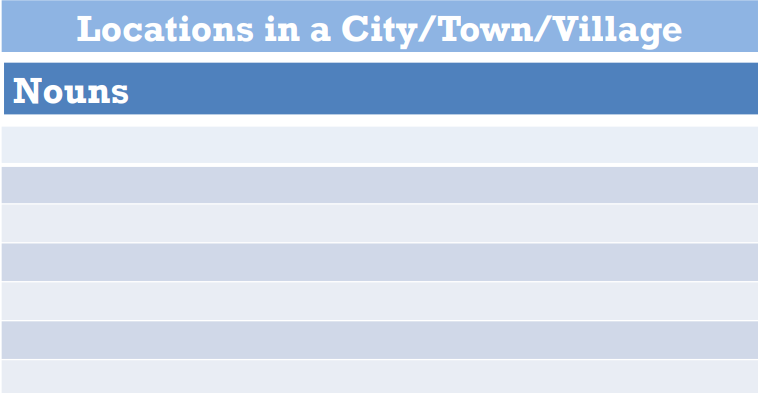
- New vocabulary (places in a town, emotions, etc.)
- Highlighting a specific grammar point (example: present perfect verbs, going to)
- Activities
- Raise hand
- Stand up
- Tally
- Categorizing

Activity 1: Listening for Vocabulary
- Assign each student (or groups of students depending on class size) one word that they will hear.
- Have students stand up (raise their hand or tally) each time they hear their assigned word. If the word is an action word, they can stand upand do the action.
Example


Activity 2: Categorizing
Example:
In chapter 1 of The Autobiography of Mark Twain, students will hear Mark Twain describe his hometown. Have students make a list of the places they hear. Next, have students listen again and make a list of all of the descriptions of the places they hear.
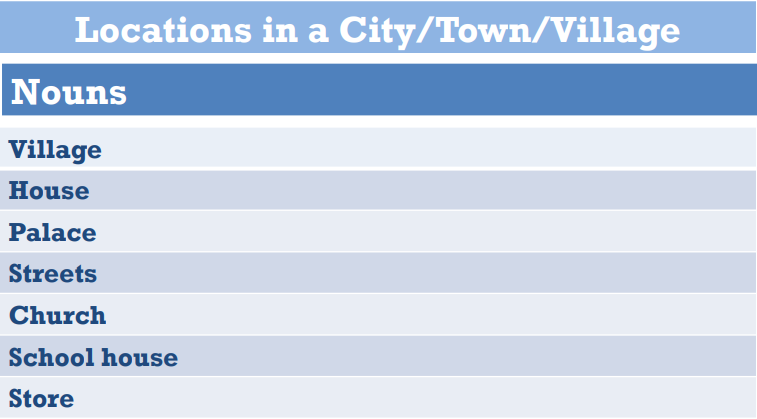
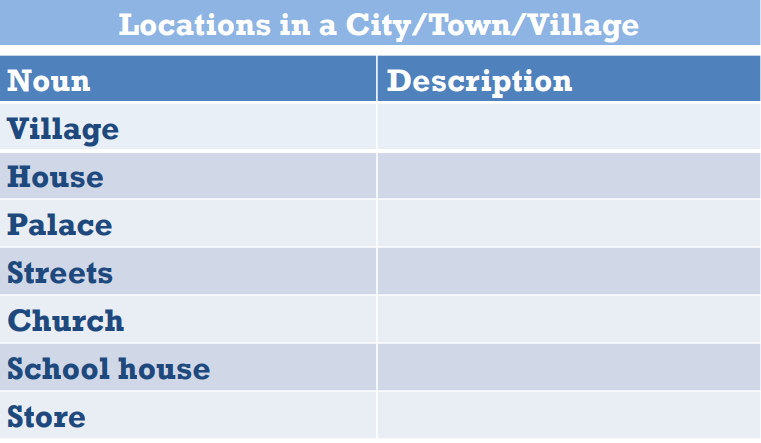

- What are some words or phrases that your students might not understand?
- What are some concept checking questions you might ask?
- Was there a palace in the town?
- Do you think Mark Twain’s house was big or small? How do you know?
- The streets were “a couple of hundred yards”? What unit of measurement (used in our country) is similar to yards (used in America)?


Activity 3: Sequencing & Summarizing
Have students listen to a segment of a story (preferably with a lot of action) 2-3 times and quickly write down what happens in the story. Next, have students rewrite what happens in complete sentences.

In pairs, have students compare their stories. In pairs, have students select 4-6 of the most important parts write their sentences on strips of paper.
Have each pair mix their sequence and trade with another group. Each group should try to sequence the other group’s cards.

Activity 4: Character Comparison
Example:
In chapter 1 of The Adventures of Tom Sawyer, students will hear Aunt Polly and Tom interact. Have students describe each character based on their interactions.

Activity 5: Predicting
Example:
In the beginning of The Gift of the Magi (0:24-0:55), students will listen to the very beginning. Then they will make a prediction (or creative story) of what they think will happen.
- Have students listen to a piece of the story 2-3 times.
- Put students in pairs or groups and have students create a scenario to finish the story
- Have students perform act 2 of the story or have students write part 2 of the story
- Other Activities:
- Chain story
- Writing a prequel

Listen Up! Using Audio Books for English Teaching for advanced Learners
Here are some audibooks sequences you can use for your lessons
Listen to the audiobooks
Paul S.Higgins: The Family Business
S. Muse: The Veil

Listen Up! Using Audio Books for English Teaching for advanced Learners
Also check out these audiobooks